What is energy? This is from U. S. Energy Information Administration.
Energy Is the Ability To Do Work
Energy comes in different forms:
- Heat (thermal)
- Light (radiant)
- Motion (kinetic)
- Electrical
- Chemical
- Nuclear energy
- Gravitational
Energy is in everything. We use energy for everything we do, from making a jump shot to baking cookies to sending astronauts into space.
There are two types of energy:
- Stored (potential) energy
- Working (kinetic) energy
For example, the food you eat contains chemical energy, and your body stores this energy until you use it when you work or play.
Energy Sources Can be Categorized As Renewable or Nonrenewable
When we use electricity in our home, the electrical power was probably generated by burning coal, by a nuclear reaction, or by a hydroelectric plant at a dam. Therefore, coal, nuclear and hydro are called energy sources. When we fill up a gas tank, the source might be petroleum or ethanol made by growing and processing corn.
Energy sources are divided into two groups — renewable (an energy source that can be easily replenished) and nonrenewable (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate). Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources can be used to produce secondary energy sources including electricity and hydrogen.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources include:
- Solar energy from the sun, which can be turned into electricity and heat
- Wind
- Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth
- Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil
- Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam
Nonrenewable Energy
We get most of our energy from nonrenewable energy sources, which include the fossil fuels — oil, natural gas, and coal. They’re called fossil fuels because they were formed over millions and millions of years by the action of heat from the Earth’s core and pressure from rock and soil on the remains (or “fossils”) of dead plants and creatures like microscopic diatoms. Another nonrenewable energy source is the element uranium, whose atoms we split (through a process called nuclear fission) to create heat and ultimately electricity.
We use renewable and nonrenewable energy sources to generate the electricity we need for our homes, businesses, schools, and factories. Electricity “energizes” our computers, lights, refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners, to name only a few uses.
Most of the gasoline used in our cars and motorcycles and the diesel fuel used in our trucks are made from petroleum oil, a nonrenewable resource. Natural gas, used to heat homes, dry clothes, and cook food, is nonrenewable. The propane that fuels our outdoor grills is made from oil and natural gas, both nonrenewable.
The chart above shows what energy sources the United States used in 2010. Nonrenewable energy sources accounted for 92% of all energy used in the Nation. Biomass, the largest renewable source, accounted for over half of all renewable energy and 4% of total energy consumption.
————————-
What is light?
This is from Optical Resources.
What is light?
It’s a kind of energy called “electromagnetic (EM) radiation” (but this kind of radiation is not harmful, except for an occasional sunburn). There are other kinds of EM radiation too (radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, etc.), but light is the part WE can see, the part that makes the rainbow.
How does light travel?
FAST and STRAIGHT.
How FAST?
About 186,000 miles per second [300,000 kilometers per second], so light from the sun takes about 8 minutes to go 93 million miles [149 million kilometers] to earth. Does this seem SLOW? Well, if you could DRIVE to the sun at 60 mph [100 kph], it would take you 177 years to get there! In one second, light can go around the earth 7 times!
How STRAIGHT?
Perfectly straight, until something bends it. The straight paths of light are called LIGHT RAYS.
How are shadows formed?
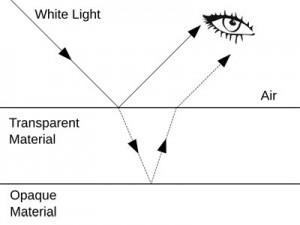
When light strikes an object, some light reflects (based on the colour of the object). when there is an obstacle in the way of the light, and it cannot pass, there is no light to reflect, and thus a shadow is formed.
A SHADOW IS FORMED WHEN LIGHT SHINES AT AN OPAQUE OBJECT BLOCKING THE LIGHT RAY CAUSING A SHADOW BECAUSE LIGHT ONLY GOES IN A STRAIGHT LINE.
Vocabulary
These are the terms for the 4th Grade Test
translucent versus transparent versus opaque:
a transparent object is one that lets light pass through (clear window)
a translucent object lets some light go through but not all (bathroom window)
opaque: light can not go through it. Impenetrable by light; neither transparent nor translucent.
an opaque object lets no light pass through (a table)
absorption: The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light. The process in which incident radiated energy is retained without reflection or transmission on passing through a medium. For example, light can not go through an object that is opaque because that object absorbs the light.
The phenomenon of a light beam rebounding after hitting a surface is called reflection. To put it simply, the mirror images are what are called reflection generally. However in the case of refraction, these angles are not the same. Different media participate in refraction, thus making this angle unequal. Reflection is found in mirrors while lenses use refraction.
light energy: energy transferred by radiation, especially by an electromagnetic wave. It’s a kind of energy called “electromagnetic (EM) radiation” (but this kind of radiation is not harmful, except for an occasional sunburn). There are other kinds of EM radiation too (radio waves, microwaves, x-rays, etc.), but light is the part WE can see, the part that makes the rainbow.
When a light wave with a single frequency strikes an object, a number of things could happen. The light wave could be absorbed by the object, in which case its energy is converted to heat. The light wave could be reflected by the object. And the light wave could be transmitted by the object.
sound energy: Sound is a type of energy made by vibrations. When any object vibrates, it causes movement in the air particles. These particles bump into the particles close to them, which makes them vibrate too causing them to bump into more air particles. This movement, called sound waves, keeps going until they run out of energy. If your ear is within range of the vibrations, you hear the sound.
pitch: pitch is the frequency at which an object vibrates to create a sound. A tuning fork, for example, that vibrates 440 times a second will produce a perfect “A” note. It is these predetermined levels of frequencies that pitch is categorized into the twelve chromatic musical tones.
vibrate: move back and forth rapidly.
Did you hear that sound? It was made by air vibrating. The same is true for sounds made by musical instruments. The difference between NOISE and MUSIC is that musical sounds are organized into patterns that have pitch and rhythm. Noise is just random, disorganized sounds. Sounds are made and travel in the same way whether they are musical sounds or noise.
A musical sound is called a tone, and is produced by air vibrating a certain number of times per second. These vibrations are called waves.
———————–
What is sound? This is from National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders.
What is sound? Sound is a form of energy, just like electricity and light. Sound is made when air molecules vibrate and move in a pattern called waves, or sound waves. Think of when you clap your hands, or when you slam the car door shut. That action produces soundwaves, which travel to your ears and then to your brain, which says, “I recognize that sound.”
This is from Science Kids at Home.
What is Sound?
Sound is a type of energy made by vibrations. When any object vibrates, it causes movement in the air particles. These particles bump into the particles close to them, which makes them vibrate too causing them to bump into more air particles. This movement, called sound waves, keeps going until they run out of energy. If your ear is within range of the vibrations, you hear the sound.
Picture a stone thrown into a still body of water. The rings of waves expand indefinitely. The same is true with sound. Irregular repeating sound waves create noise, while regular repeating waves produce musical notes.
When the vibrations are fast, you hear a high note. When the vibrations are slow, it creates a low note. The sound waves in the diagram show the different frequencies for high and low notes.
Low frequency notes |
High frequency notes |
How do Wind Instruments make sound?
In wind instruments, like the flute and trumpet, vibrating air makes the sound. The air particles move back and forth creating sound waves. Blowing across a flute’s blow hole sets up Slinky-like waves in the tube. In the clarinet, a vibrating reed (a thin piece of wood set in the mouthpiece) gets the waves started. Different pitches are played by pressing keys that open or close holes in the tube making the air column inside the tube longer or shorter. Longer air columns produce lower pitches.
How do String Instruments make sound?
Stringed instruments are played by pressing the fingers down on the strings. This pressure changes the strings’ length, causing them to vibrate at different frequencies and making different sounds. Shortening a string makes it sound higher. Strings produce different sounds depending on their thickness.
————————
Forms of Energy. This is from U. S. Energy Information Administration
Forms of Energy Basics
What Is Energy?
Energy makes change possible. We use it to do things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and lights our homes. Energy is needed for our bodies to grow and it allows our minds to think.
Scientists define energy as the ability to do work. Modern civilization is possible because we have learned how to change energy from one form to another and use it to do work for us and to live more comfortably.
Forms of Energy
Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic.
Potential EnergyPotential energy is stored energy and the energy of position — gravitational energy. There are several forms of potential energy. |
Kinetic EnergyKinetic energy is motion — of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances, and objects. |
|---|---|
| Chemical Energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Batteries, biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and coal are examples of stored chemical energy. Chemical energy is converted to thermal energy when we burn wood in a fireplace or burn gasoline in a car’s engine.Mechanical Energy is energy stored in objects by tension. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands are examples of stored mechanical energy.Nuclear Energy is energy stored in the nucleus of an atom — the energy that holds the nucleus together. Very large amounts of energy can be released when the nuclei are combined or split apart. Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms in a process called fission. The sun combines the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in a process called fusion.Gravitational Energy is energy stored in an object’s height. The higher and heavier the object, the more gravitational energy is stored. When you ride a bicycle down a steep hill and pick up speed, the gravitational energy is being converted to motion energy. Hydropower is another example of gravitational energy, where the dam “piles” up water from a river into a reservoir. | Radiant Energy is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Radiant energy includes visible light, x-rays, gamma rays and radio waves. Light is one type of radiant energy. Sunshine is radiant energy, which provides the fuel and warmth that make life on Earth possible.Thermal Energy, or heat, is the vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules within substances. As an object is heated up, its atoms and molecules move and collide faster. Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth.Motion Energy is energy stored in the movement of objects. The faster they move, the more energyis stored. It takes energy to get an object moving, and energy is released when an object slows down. Wind is an example of motion energy. A dramatic example of motion is a car crash, when the car comes to a total stop and releases all its motion energy at once in an uncontrolled instant.Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate — the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave. Typically, the energy in sound is far less than other forms of energy.Electrical Energy is delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, typically moving through a wire. Lightning is an example of electrical energy in nature, so powerful that it is not confined to a wire. |


Leave a Reply